Table Of Contents
- What is a TP Order?
- What is an SL Order?
- Risk-Reward at a Glance (Why TP and SL Work Best Together)
- Where and When Can I Use a TP and SL?
- Quick Setup Flow (Step-by-Step)
- Technical Indicators That Help Set TP and SL
- The Importance of Risk Management and Trading Psychology
- The Importance of Preserving Capital
- Determining When to Use TP
- The Role of Fundamental Analysis in Setting TP
- Psychological Price Points and Their Impact on TP levels
- Types of SLs
- Pros and Cons of Using TP and SL
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- The Bottom Line
What Are Take-Profit and Stop-Loss Orders? How Do They Work?
In my view, as an experienced trader, risk management is one of the most important things to learn for new traders. Mastering it will ensure the longevity and success of everything you do in the financial markets. Without a disciplined approach to managing potential losses, even the most well-researched trading strategy can quickly go bad.
A new trader might ask, “Why is it so important to understand risk management?” Unlike large financial institutions, retail traders often have limited capital. This makes you vulnerable to swings in financial markets. A robust risk management strategy not only protects your capital but also provides a psychological comfort blanket. It ensures that your trading decisions remain calculated rather than impulsive.
Yes, spotting profitable opportunities is a good skill, but preserving capital is what sets the best traders apart from the rest. In this article, I will introduce you to two important risk management tools: take profits (TP) and stop losses (SL). I will also explain how you can use them in trading.
TTP and SL orders are essential tools for managing risk and protecting capital in every trade
A TP order locks in profits automatically once your asset hits a predefined price
An SL order cuts your losses at a price you’re willing to accept if the trade goes against you
Using TP and SL helps remove emotional decision-making by setting clear exit points before a trade begins
You can apply TP and SL across assets like FOREX, stocks, commodities, crypto, and more
Trailing stops let your profits grow while still protecting your downside as prices move in your favor
Tight stops and arbitrary profit targets are common beginner mistakes that can limit your success
Always combine TP and SL with solid technical and fundamental analysis for the best results
What is a TP Order?
I believe that TPs and SLs are two of the most important risk management features in the world of trading. They are excellent tools you can use to preserve your capital. A TP is a predetermined price level set by a trader at which they aim to close an open position for a profit. Think of it as a target price you expect the asset to reach; once it hits that price, the position is automatically closed. This guarantees that you take a desired level of profit. Yes, the instrument could continue to be profitable after your target price, but inserting a TP means you won’t go chasing riches.
What is an SL Order?
On the other hand, an SL is an order placed with a broker to buy or sell once the asset reaches a certain price that is going against you. This feature is best for limiting your loss on a position. The SL is typically set at a price lower than the current market price. If the deal doesn't go as planned, the SL order will automatically trigger, closing the position and capping the loss at a predefined amount.
Risk-Reward at a Glance (Why TP and SL Work Best Together)
As I’ve said, successful trading is about controlling the downside while giving the upside room to grow. That’s where the combination of TP and SL orders works best. Used together, they draw a clear boundary around your trade: you know upfront how much you’re willing to risk and what kind of return you seek.
The most common framework traders use is the risk-to-reward ratio. Imagine you enter EUR/USD at 1.0800, set your stop-loss at 1.0780, and your take-profit at 1.0860. You’re risking 20 pips to potentially make 60, which is a 1:3 risk-reward setup. In practical terms, you could be wrong twice and right once, and still come out ahead. There is a certain elegance to this risk-reward setup.
Now balance that with the idea of a poor setup, risking 50 pips for a potential gain of only 20. Even with a high win rate, your account would bleed over time. The graphic below illustrates a 1:2 risk-reward setup, with the SL accepting a certain level of risk and the TP accepting double that risk in the form of a reward.
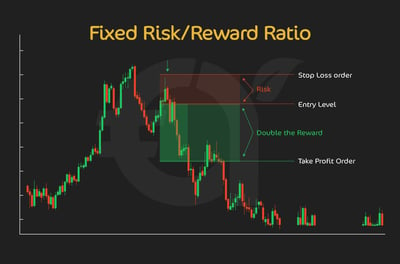
I would say this is why professional traders emphasize ratios over outcomes. They’re less concerned with each individual trade and more focused on the long-term math. A consistent 1:2 (like the one shown in the graphic) or 1:3 ratio means you don’t have to win every trade to grow your equity curve. In fact, you can be wrong more often than right and still finish in profit!
Where and When Can I Use a TP and SL?
As I've done in my trading career, you can use TPs and SLs across various financial instruments. This is the best way to automatically lock in profits or limit losses. Here are some of the instruments where these orders are commonly used:
FOREX: This is one of the most popular markets where TP and SL orders are used. FOREX traders can set these orders to protect their positions from sudden currency price swings.
Stocks: Day traders or swing traders on the stock market often use these orders.
Commodities: Whether it's oil, gold, or agricultural products, traders in the commodities market make the most of TP and SL orders to manage their trades.
Futures Contracts: Futures traders can also set TP and SL orders to manage the risks that come with volatile price movements.
Options: While options traders might not use TP and SL in the same way as do traders in other markets, they can still set certain price levels to automatically close out positions.
Contract for Differences (CFD): These complex derivative instruments allow traders to speculate on the price movement of an asset without owning the asset itself. TPs and SLs come in very handy during CFD trading.
Cryptocurrencies are among the most volatile trading assets. Traders frequently manage their risk in cryptocurrency markets with TPs and SLs.
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): Just like with stocks, ETF traders can set these orders to automatically close positions at predetermined levels.
Bonds: This activity may be less common than in other markets, but bond traders can also use TP and SL orders, especially on electronic trading platforms.
Quick Setup Flow (Step-by-Step)
So, how do you set up TPs and SLs? Sequentially, you should:
Research the instrument,
Define entry,
Decide on the invalidation point (SL), and
Decide on the objective (TP), then
Size the position, and
Place the orders.
The simplest way to bring discipline into your trading is to treat SL and TP orders as inseparable parts of the same plan. It starts with research: know your instrument, whether it’s EUR/USD trading at 1.0850, gold pushing past $2,400, or Tesla stock testing a breakout.
Once you’ve defined your entry, the next step is to mark your invalidation level, where the trade idea is proven wrong. That’s your SL. Then you set your objective, the price level that rewards the risk you’re taking. That’s your TP.
Sizing the position comes next. If you’re risking 1% of your account and your stop-loss is 50 pips away, you calculate how many lots fit inside that boundary. This math ensures that no single loss reduces your equity below what you can tolerate. With your risk defined and your reward targeted, you place both orders alongside your entry. The plan goes live from the start, and the market decides the outcome without you second-guessing every tick.
The real point is that pairing these orders together creates a bounded trade. You know what you stand to lose and what you hope to gain before the market moves. The following graphic shows what a TP and SL setup looks like on many common trading platforms.
.webp)
By locking in your exit rules at the same time you open the trade, you’re eliminating the temptation to move stops wider or chase extra pips, habits that often destroy accounts. Instead, your trade runs on math, not emotion, and that is where long-term consistency comes.
How to set TP and SL on MT4?
When trading on MT4, you can set a TP and SL when placing a new order by entering your chosen price levels in the appropriate fields before executing the trade. If you already have an open position, simply right-click on the order in the “Terminal” window, select “Modify or Delete Order,” and enter your TP and SL levels there.
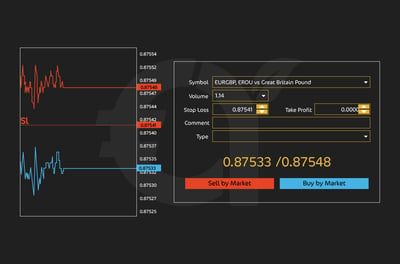
The stop-loss should be placed at a price that limits your loss to an acceptable level if the market moves against you, while the take-profit should lock in gains once the price reaches your target. MT4 will automatically close your trade at these levels, giving you better control over risk and reward without needing to constantly monitor the market. Here’s a graphic showing TP and SL market execution levels of 0.87533 and 0.87548 respectively:
Technical Indicators That Help Set TP and SL
While traders can set SL and TP levels using intuition or fixed percentages, technical indicators provide a more objective lens. Indicators measure volatility, trend direction, and momentum, offering logical levels where price is more likely to stall or reverse. Four of the most common methods involve support and resistance, moving averages, Fibonacci retracements, and MACD signals. We’ll discuss them next.
How to set SL and TP using support and resistance indicators
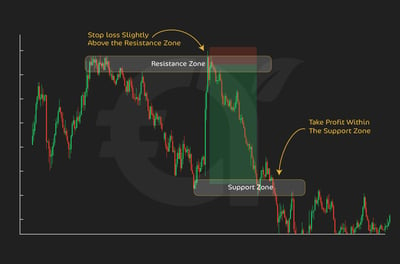
In my opinion, one of the most straightforward tools for defining exit points is the support and resistance indicator. When you go long, a logical place for a stop-loss is just below the nearest support zone, since a break beneath that level invalidates the bullish setup.
TP is often placed just below the resistance level, where sellers are expected to step in. For example, if EUR/USD is trading at 1.0850, with support at 1.0820 and resistance at 1.0900, a trader might set a stop at 1.0815 and a take-profit at 1.0890. This creates a natural boundary based on market structure rather than arbitrary numbers. The key is to respect these levels, as collective trader psychology often clusters orders there. The graphic below shows how to work with support and resistance levels.
How to set SL and TP using the moving average indicator
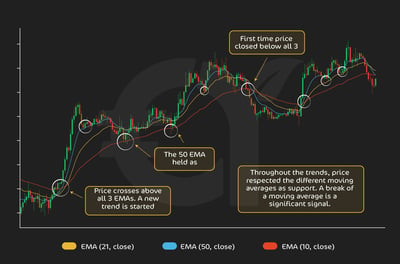
Moving averages act like dynamic support and resistance, particularly when markets trend. A trader buying above the 50-day moving average might place a stop just below that line, assuming the trend holds as long as the average is not breached. TP targets can be set at the next higher moving average or at recent swing highs aligned with the trend.
Moving averages often “work” less because of magic and more because of crowd behavior. Price action tends to respect them simply because so many traders watch and trade off the same levels. That’s why sticking with the most commonly used moving averages, like the 50, 100, or 200, is critical. Their real power comes from the self-fulfilling effect of mass participation, where following the crowd can actually improve your edge.
In our moving average article, we discussed the simple moving average (SMA) and the exponential moving average (EMA). The graphic below shows how you can use these as guideposts to understand when they are acting as support or resistance. See how the 50-day EMA acts as support for the trend shown.
How to set SL and TP using the Fibonacci Indicator
Fibonacci retracements and extensions are popular for measuring how far a market might pull back or rally. In an uptrend, traders often place stops just below a retracement level, say the 61.8% line, while aiming to take profit at extension levels such as 127.2% or 161.8%. Fibonacci indicators help bring structure to otherwise unpredictable moves, creating mathematically derived exit points that align with how many traders view markets.
I recommend that when using Fibonacci retracements, a smart way to protect your trade is to place your stop-loss just beyond the next Fibonacci level. For instance, if you short at the 38.2% retracement, you’d tuck your stop just past the 50%. Similarly, if you enter at the 50%, and you’d place it past the 61.8%. If you go in at 61.8%, and your stop sits beyond 78.6%. We’ve shown one example in the graphic below.
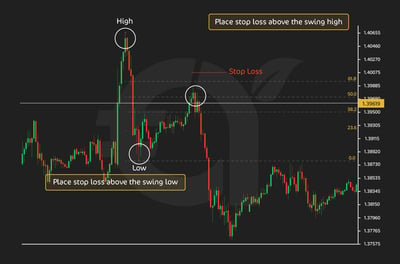
The logic is simple: if the level you trusted as support or resistance fails, your trade thesis is invalid, and the stop saves you from deeper losses. It’s not foolproof, the market can easily spike, trigger your stop, and then move in your favor, but that’s the trade-off. This method works best for short-term setups, especially intraday, where price action around key Fibonacci levels tends to be more reliable.
How to set SL and TP using the MACD Indicator
MACD, which tracks momentum and trend strength, can guide stop and target placement based on signal shifts. When the MACD line crosses above the signal line, traders may enter long with a stop beneath the recent low, keeping risk tight in case momentum fails. The TP can be set at the next point where MACD historically turns down, often aligning with prior peaks. For instance, if the S&P 500 shows a bullish MACD crossover at 4,800, with recent support at 4,760, the stop could sit just under that floor, while the TP might be targeted near 4,950, where MACD peaks in past cycles. The beauty of MACD is that it captures both trend direction and fading momentum.
Look at this image below. The chart highlights three past signals on AUD/USD, with the indicator about to issue a fourth. When trading with the MACD, a SL is often set just beyond the recent swing high or low that preceded the MACD crossover, ensuring you’re out if momentum clearly shifts against you.
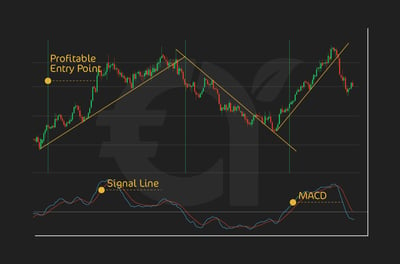
TPs, on the other hand, are best placed before obvious support or resistance levels, or when the MACD histogram shows signs of waning momentum. In essence, your SL protects you when the trade idea is invalidated, while your TP locks in gains before the market turns—both working hand in hand to keep you disciplined.
The Importance of Risk Management and Trading Psychology
Here at Arincen, our experts understand that emotions like fear, greed, hope, and regret can significantly influence your trading behavior, and not always in a good way. Fear can make you sell off assets prematurely during a market downturn, potentially missing out on rebounds. On the other hand, greed can make you hold onto positions for too long, only to see gains diminish or turn into losses.
How TP and SL can help curb emotional decision-making
TP and SL orders can counteract the dangers of emotional decision-making. If you understand the realities of human trading psychology, you will know that it is normal for human traders to be swayed by emotions. That's why you need to work according to a robust trading plan. By setting predetermined exit points, both for potential profit and acceptable loss, traders establish a clear framework for their trades, which acts as a barrier against the whims of emotional impulses. A TP ensures that profits are secured at a specific target. Conversely, an SL provides a safety net, ensuring that in the face of adverse market movements, losses are capped at a level with which the trader is comfortable.
The Importance of Preserving Capital
For the newbie trader, preserving capital is vital. Here's why believe this:
When starting out, a trader's primary capital is both their lifeline and their tuition. In the ever-evolving world of trading, mistakes are inevitable, especially in the initial stages. Preserving capital ensures that new traders have the leeway to learn from these mistakes without being completely sidelined by them.
Preserving capital ensures longevity in the trading arena. The longer you are in the business, the more experience you gain.
Trading, especially in its early stages, can be as much a psychological challenge as it is a technical one. Experiencing substantial losses can be emotionally taxing and can erode confidence. By focusing on capital preservation, newbie traders can maintain a more stable emotional state, which is crucial for making rational decisions.
Determining When to Use TP
There is a skill to deciding when to use a TP. When traders first start, much of what they do is based on guesswork. This is completely normal and expected. As you gain more experience, you get to grips with using additional tools, like technical analysis, to help support your decisions. In the image below, see how the TP can be safely set at 1.3741, which gives the trader a decent return after the buy trade level of 1.37250.
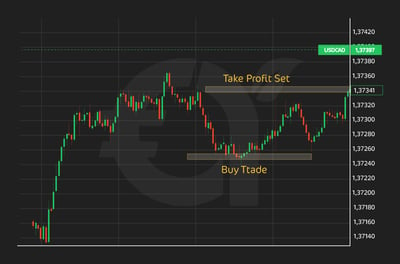
I've heard some people liken trading to trying to predict where a ball might bounce or stop rolling on a playground. To do that, traders often use previous patterns they have seen before. They apply this technical analysis to determine important markers such as support and resistance levels of a financial asset. These are its lowest and highest levels, respectively. By watching these patterns and using these tools, traders set their profit targets and decide when to buy or sell to make the most money. If you get really good at technical analysis, you could even get to a point where advanced tools like Fibonacci indicators inform your trades.
The Role of Fundamental Analysis in Setting TP
While technical analysis is all about studying past data, you can think of fundamental analysis as the "health report" of a stock or an asset. Fundamental analysis looks at big news like economic announcements or how much profit a company makes. If a company announces big profits or if there's positive economic news, the stock might rise. So, traders use this information to set their TP points. For example, Nvidia is a stock in the news right now as it is posting record earnings based on the rush by industries to adopt artificial intelligence. If you weren't paying attention to the news, you would not know when to back this stock.
Psychological Price Points and Their Impact on TP levels
Imagine walking into a store and seeing a price tag of $9.99 instead of $10. Even though it's just a penny less, it somehow feels like a better deal, right? This is due to psychological price points – prices that feel more attractive or significant to us.
In trading, these psychological points, like round numbers, are often where traders decide to take their profits. For instance, a stock approaching $100 might see many traders set their take-profit just below that level. This is because it's a big, round, and memorable number. Humans are very much alike in these types of preferences. So, just as a $9.99 price tag attracts shoppers, these psychological levels in the market can attract traders and influence where they decide to cash in.
Types of SLs
While there is really only one way to take profit, there are multiple ways to insert an SL:
Hard SL: A firm price level
A hard SL in trading is a firm price level at which you've decided in advance to sell your stock or asset to prevent further losses. No second-guessing, no waiting, once it hits that set level, you're out. It's a trader's safety net, ensuring they don't stay on a financial ride that's getting too wild for their comfort.
Trailing Stop: Moves with the price in a profitable direction
A trailing stop is a way to let your profits run, while still having a safety mechanism to guard against major losses. As your investment or stock price climbs, the trailing stop adjusts and moves up with it, securing your gains. But if the stock price starts to drop, the trailing stop acts as a limit order, automatically selling your stock before it falls too much.
Mental Stop: Based on the trader's discretion, not placed with the broker
A mental stop is another one of those human shortcuts we like to use. A mental stop is a price level at which a trader decides to sell an asset if its price drops to that level. However, unlike other stops, this isn't necessarily set on the broker’s platform. Instead, it's based on your personal judgment. There is a risk to doing this, as you must then manually make the sale when that point is reached. This approach is mainly for active traders who have the self-discipline to know when to sell up.
Stop-Loss vs. Stop-Limit: What can go wrong
Traders often confuse stop-loss and stop-limit orders, but the difference matters most when markets move fast. A stop-loss becomes a market order once the trigger price is hit. That gives it a high probability of execution, but in volatile conditions, the actual fill can slip far from the trigger. A stop-limit adds a limit price to the trigger, meaning the order only executes within your specified range. That protects you from extreme slippage, but if the market gaps through your limit, the order may not execute at all, leaving you stuck in a losing position. The trade-off is clear: one prioritizes certainty of exit, the other prioritizes price control.
When to Use Which
If closing the position is non-negotiable, such as holding a stock into an earnings release or sitting on a leveraged FOREX trade before a central bank decision, the plain stop-loss is the safer tool. Even with slippage, you know you’re out of the market and your downside is capped. By contrast, if price is more critical than certainty, such as in illiquid small-cap stocks or thinly traded commodities, a stop-limit gives you control over the minimum or maximum fill. The risk is that a gap leaves you exposed, still holding the trade while the market runs against you.
Professional traders weigh this decision based on the nature of the instrument, the volatility backdrop, and their own risk tolerance. The wrong choice can mean either taking a worse fill than expected or, worse, no fill at all.
Pros and Cons of Using TP and SL
In my experience, here is what you need to know about the pros and cons of using these tools:
Pros
Emotional buffer: TP and SL orders help take the emotion out of trading decisions. It gives you a systematic approach that reduces impulsive reactions based on fear or greed.
Risk management: SL orders limit potential losses by automatically selling an asset when its price drops to a certain level, ensuring that you don't suffer major financial setbacks from a single trade. Risk management is a crucial way to extend your trading career.
Profit locking: TP orders allow traders to secure profits automatically when a price target is achieved. This way, gains aren't eroded if the market shifts in the opposite direction.
Efficiency: Both orders allow for automated trading, meaning positions can be closed even if you are away from your screen. This ensures that even in fast-moving markets, you can safely take your eye off the trading screen for a while.
Cons
Premature exits: Market volatility can trigger an SL or TP prematurely, potentially causing a trader to miss out on further profit or exit a position before a potential rebound. This happens fairly frequently, and traders kick themselves when it happens, but these are the ebbs and flows of trading.
No flexibility in real-time analysis: Once you have set them, TP and SL might prevent traders from taking advantage of changing market conditions or new information that affects a market price.
Slippage: This is an important thing to remember about volatile markets, like FOREX and cryptocurrencies. The actual execution price of SL or TP orders might differ from the set price, leading to unexpected losses or reduced profits.
Over-reliance: It’s easy to develop an over-dependence on these orders and neglect keeping a pulse on the market and educating yourself.
False security: Some traders may feel overly protected by these tools and engage in riskier trades than they otherwise would, believing they have a safety net in place.
While TP and SL orders offer essential tools for risk management and strategy execution, how well they work really depends on accurate application combined with broader trading strategies.
Execution Realities
In theory, stop orders give you protection. In practice, execution can get messy. A stop-loss converts into a market order once triggered, which means it will usually fill, but often at a worse price if the market gaps or liquidity thins. A stop-limit avoids slippage by enforcing a ceiling or floor, but if the price jumps straight through that limit, the order never executes, leaving you exposed. Trailing stops add another twist: they adjust dynamically with the market, helping you ride a trend while locking in profit. They also reduce the frustration of being stopped out just before the market reverses, a common pain point in choppy conditions. Still, no stop type is perfect; you trade off certainty, price control, and flexibility depending on your choice.
Platform Mechanics and Constraints
Stops also depend heavily on platform rules, which many traders don’t know about. Some platforms trigger stops based on the last traded price; others on bid, ask, or a “mark” price that smooths volatility. Margin checks happen at the moment of trigger, so if your account doesn’t have the required funds, the order can be rejected.
On most derivatives platforms, brokers often enforce minimum stop distances, say, 10 ticks away from the current price, or fixed offsets that prevent ultra-tight stops. These constraints are designed to protect both trader and broker, but they can interfere with strategy if you’re not aware of them. The lesson is simple: before trusting automation with your capital, know exactly how your broker defines and executes stop orders. The fine print can be the difference between clean risk management and an unwanted surprise.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
I must stress that while TP and SL are invaluable tools for traders, they are not perfect. A successful trading strategy incorporates these tools while also allowing for flexibility and continuous learning. You still need to be able to think on your feet. Here are some common errors:
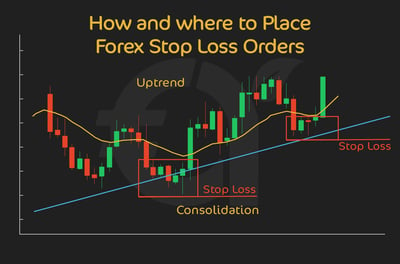
Setting Stops That Are Too Tight: One of the most common mistakes, especially among new traders, is setting their SL levels too close to their entry point. Often, this results in your position being closed too early in response to normal market volatility, even if the overall trend is in the trader's favor. It’s a newbie trap that you can only get out of with more trading experience. A simple analysis method to help you avoid this mistake is the moving average, which could give you the information you need to relax your stops a little.
How to Avoid: Ensure your SL is set at a level that gives the trade some room to breathe. This might involve analyzing the asset's average volatility and setting the SL slightly beyond that.
Neglecting to Adjust: As a trade becomes profitable and moves in the desired direction, some traders forget to adjust their SL to protect their gains, leaving them vulnerable to market reversals.
How to Avoid: This is a textbook occasion to use a trailing stop, which moves with the price in the profitable direction, automatically adjusting the SL level as the price moves favorably. You could also use trading channel analysis to keep you better in the loop.
Setting Arbitrary Targets: Sometimes, traders set TP levels based on desired profit amounts rather than actual market analysis. This happens more frequently than traders like to admit. This can either cut profits short if set too low or leave you waiting for a target that the market has no real reason to reach.
How to Avoid: Base your TP levels on sound technical or fundamental analysis. Look for logical points of resistance or potential market turnarounds rather than pie-in-the-sky profit numbers. One technical analysis tool that could help you set a defined target is Bollinger Bands.
Ignoring Major News Events: Economic announcements or significant company news can lead to sudden and drastic market movements. If you are not ready, these can sweep past TP or SL levels.
How to Avoid: Always stay up to date on the economic calendar and major news events. Consider widening SL or TP levels during these times or avoiding trading altogether.
Over-relying on Mental Stops: While mental stops can be useful, relying solely on them can be problematic. Emotional biases can prevent you from executing your exits when the predetermined level is reached.
How to Avoid: Use actual SL orders whenever possible. They enforce discipline and ensure you stick to your trading plan, even when emotions run high.
Not Re-evaluating: As time passes and more information becomes available, the initial TP and SL levels may no longer be appropriate. Sticking rigidly to old levels can hurt you.
How to Avoid: Continually reassess your positions when new data is presented. As the market landscape changes, so should your targets.
Using Stop-Limit as “Protection”: Don’t assume a stop-limit order is a foolproof safety net. It feels safer because you’re telling the market the worst price you’re willing to accept. The problem arises when the market skips past your limit. Instead of closing your position at a controlled loss, you’re left holding the trade as it bleeds further.
How to Avoid: Always remember that a stop-limit prioritizes price, not execution. If closing the trade is paramount, think earnings releases, central bank announcements, or high-volatility events; stick with a plain stop-loss even if it risks some slippage. Save stop-limits for instruments where liquidity is thin and you’re willing to accept the chance of no fill in exchange for stricter price control.
The Bottom Line
In my trading experience, TP and SL orders are among the most crucial steps for traders, providing a structured approach to maximizing gains and minimizing losses. Yet, as with any powerful tool, how well they work depends not only on how they are used but also on their consistent application. The nuances of setting, adjusting, and re-evaluating these orders can mean the difference between flash-in-the-pan success and sustained profitability.
By understanding the intricacies of TP and SL, and by sidestepping common pitfalls, you not only safeguard your capital but also master the art of trading with accuracy and foresight. This is one of the best ways to have a long and fruitful trading career.
FAQ
An SL is designed to limit downside by closing a losing position once the price reaches your set level. A TP does the opposite; it locks in gains when the price reaches your target. Together, they define your risk and reward before the trade even begins.
Yes, but it’s not ideal. A SL alone protects you from large losses, but without a take-profit you rely on judgment to exit winners, which often leads to emotional decisions. Pairing both creates structure: you know when you’re wrong and when you’re right.
Many traders aim for at least 1:2, meaning they risk $1 to make $2. Ratios like 1:3 are even stronger, allowing you to be wrong more often than right and still grow your account. Anything less than 1:1 tends to eat into long-term profitability.
Not always. In liquid markets, they usually do. But in fast-moving or gapping markets, your fill can slip to the next available price. This is the trade-off for execution certainty.
A stop-limit may not execute at all if the market gaps through your limit. That leaves you exposed while price runs against you. Stop-limits are best reserved for illiquid assets where price is more important than certainty of exit.
You can, but moving it wider to “give the trade more room” is usually a mistake. Moving it tighter to lock in profit, often called a trailing stop, can be a disciplined way to ride trends. The key is having rules, not improvisation.
Indicators like moving averages, Fibonacci levels, and MACD provide logical zones where price often stalls or reverses. Using these tools means your exits are not random but instead are grounded in market structure and probability.
No tool is perfect. Stop-losses can slip, stop-limits can fail to fill, and even TPs can miss in fast markets. But they remain the most reliable way to enforce discipline and remove emotion. Without them, your account is at the mercy of instinct and luck.


